SIP trunking
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunking is a digital communications technology that allows businesses to make phone calls over the Internet instead of traditional phone lines. Instead of using physical wires, SIP trunking sends voice data over the internet as packets of information. This can save businesses money on long-distance and international calls. SIP trunking also allows businesses to have greater flexibility and scalability in their phone systems as they can easily add or remove lines as needed. SIP trunking offers a more modern and efficient way for businesses to communicate with their customers and employees.
Businesses typically use SIP trunking for:
- Cost savings: SIP trunking can save businesses money on long-distance and international calls
- Scalability: SIP trunking allows businesses to easily add or remove lines as needed, making it a scalable solution for growing businesses
- Business continuity: SIP trunking can provide redundancy and failover options, ensuring that businesses can continue to make and receive calls even during an outage
To use SIP trunking, you need:
- An IP-based Private Branch Exchange (PBX) system - this is the phone system that manages internal and external calls - or an SBC (Session Border Controller) - which acts as a firewall between your internal network and the internet
- A reliable internet connection: since SIP trunking relies on the internet to make and receive calls, a stable and fast internet connection is crucial
Use cases with SIP trunking
Multiple usage scenarios can be considered:
| Use case category | Use case | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Global reach and connectivity | Outbound (termination) | Use your SIP infrastructure to send call requests to the Infobip platform that we terminate on PSTN destinations across the world. Infobip offers the widest reach of connectivity on the planet, with more than 200 countries in its global reach and nine geographically dispersed data center locations accepting your SIP trunk connections in self-service. |
| Inbound (origination) | Rent local DID numbers from Infobip, and calls received on these numbers are forwarded to your SIP infrastructure. | |
| Programmable SIP | SIP trunk management | Although SIP trunks can be fully managed from the Infobip web interface, you can integrate and automate the management of your trunks using our API (creation, update, and deletion). |
| Your voice application | When using the Calls API platform to develop a voice application that implements your exact scenario, your application can process inbound calls coming from your SIP trunks and create outbound calls to SIP endpoints. |
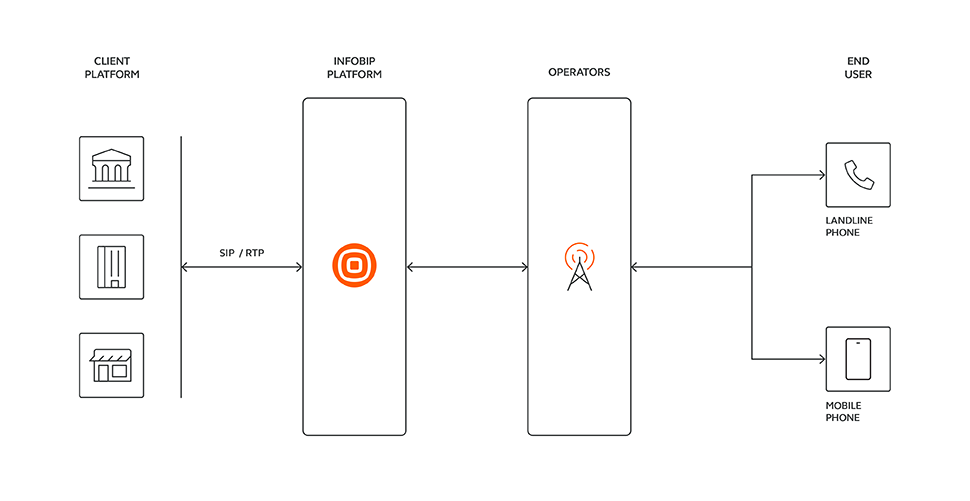
Supported SIP trunk types and characteristics
Infobip supports SIP trunking to multiple environments.
| SIP trunk provider | Use case | Type | Configuration | Authentication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INFOBIP | Connect to your own on-premise or cloud hosted PBX or SBC. | Static | Requires manual configuration of the trunk settings such as IP addresses, port number, codecs and DTMF/Fax transcoding. | Uses IP-based authentication where Infobip trusts traffic from your declared IP addresses. |
| INFOBIP | Connect to your own on-premise or cloud hosted PBX or SBC. | Registered | Configured dynamically through the registration process between your PBX/SBC and our servers. Requires manual configuration of the trunk settings codecs and DTMF/Fax transcoding. | Uses username and password authentication to validate the PBX/SBC's identity. |
| Freshworks | Connect to Freshcaller from Freshworks. Freshcaller uses Twilio as its communication engine. See How to configure BYOC for more details. | N/A | Requires your Twilio Account SID and Twilio SIP domain. Other parameters such as codecs, dtmf and fax transcoding settings are preset. | Twilio Account SID and traffic source. |
| Genesys PureCloud | Connect to your Genesys PureCloud environment. | N/A | Based on the selected Genesys region, the trunks will be automatically mapped to the adequate Infobip data center. | Genesys region, Inbound SIP termination identifier and Outbound SIP termination FQN. |
| Cisco Webex | Connect to your Cisco Webex environment. | N/A | Available in the USA only. | Requires your Cisco Customer Organizational ID (UUID). |
| OpenAI Realtime | Connect to OpenAI Realtime API over SIP for your voice AI agent projects. | N/A | Requires your OpenAI Project ID. | Requires your OpenAI Project ID. |
When configuring an Infobip static SIP trunk to connect to your SBC or PBX, it is essential to provide public and dedicated IP addresses. These IP addresses must be:
- Publicly routable on the internet: not behind NAT or within private subnets
- Exclusively assigned to your infrastructure: not shared with other customers
Infobip does not support configurations where SBC or PBX systems are hosted in shared environments, where IP addresses may be dynamically allocated or used by multiple tenants. To ensure security, stability, and routing integrity, your endpoint must have a static, dedicated IP address.
SIP trunk channels and related billing plans
When creating a SIP trunk, you need to define the number of channels to be allocated. A channel represents a single concurrent call, so a 10-channel trunk means 10 concurrent calls can take place at any moment in time, whether inbound and/or outbound. Calls submitted to the trunk when the trunk has reached its channel capacity will be rejected.
You can choose between two different channel plans: metered or unlimited.
Metered channel plan
With the metered plan, the pricing per channel is unique whatever the call destination or location of the SIP trunk (Infobip hosting data center).
The voice traffic (between Infobip and the telco operators) is billed by usage, whatever the destination or origination.
Unlimited channel plan for US domestic traffic
With the unlimited channel plan, the outbound US domestic voice traffic is not charged by usage (subject to fair use policy). Any traffic to or from other countries will be billed by usage.
Technical requirements
SIP methods
The following SIP methods are currently supported:
- INVITE and reINVITE
- ACK
- BYE
- CANCEL
- OPTIONS
Transport
The following transport mechanisms are supported:
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol): a connectionless transport mechanism to transmit voice data between endpoints. It is a lightweight and fast protocol that doesn't require any handshaking or acknowledgment of received packets, which makes it ideal for real-time applications like voice calls. However, UDP is also less secure than other protocols, as it doesn't provide encryption or authentication of packets.
- TLS/SRTP: TLS (Transport Layer Security) and SRTP (Secure Real-time Transport Protocol) are more secure transport mechanisms that use encryption and authentication to protect against eavesdropping, tampering, and other security threats. TLS is a protocol that encrypts the SIP signaling traffic between the PBX and our infrastructure, while SRTP encrypts the voice traffic itself. Both TLS and SRTP require a handshake and verification process between endpoints, which can cause some latency and overhead, but provide higher security and privacy.
Codecs and transcoding
| Type | Support |
|---|---|
| Media | G.711a (PCMA): high-quality audio with low latency (8khz sample rate and 64kbps bit rate) |
| Media | G.711µ (PCMU): high-quality audio with low latency (8khz sample rate and 64kbps bit rate) |
| Media | G.729: for networks with limited bandwidth, requires additional processing power (8khz sample rate and 8kbps bit rate. Uses a compression algorithm to reduce the bit rate while maintaining acceptable audio quality) |
| DTMF | RFC2833: sends DTMF separately from the audio stream using dedicated RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol) event message. Allows for more precise transmission of the DTMF signals, and better compatibility with various network configurations and PBX systems. Increases the overall bandwidth usage and may require additional setup and configuration. |
| DTMF | Inband DTMF: DTMF signals are transmitted as part of the audio stream, using the same frequency range as the voice data. Simple and widely supported, but can lead to distortion or clipping of the audio signal, particularly in low-bandwidth or noisy environments. |
| Fax | T38: separates the fax signal from the audio signal and transmits it as a separate stream using UDP or TCP. Most reliable and error-free. |
| Fax | Inband: transmits fax data as part of the audio stream using the same frequencies as voice data. Can lead to error and distortion in low-bandwidth or noisy environments. |
SIP trunking redundancy
Infobip provides multiple levels of redundancy for SIP trunks and routing of DID to SIP. At a high level, these capabilities fall into three categories.
| Redundancy Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Infobip SBC redundancy | For each SIP Trunk you order, Infobip provisions the trunk on two geographically-redundant SBCs within its core network. Upon failure of the primary SBC, calls automatically route to/from the secondary SBC. This capability is currently limited to Infobip's USA data centers. |
| Your SBC/PBX redundancy | Static SIP trunks can be defined with multiple destination IPs (fixed public IPs that are exposed by you) and distribute calls according to your chosen policy (such as round-robin or failover).If you have redundant infrastructure in your network, you may also order multiple SIP trunks and source calls from either SIP Trunk. |
| Infobip Call Routing | If you have redundant infrastructure in your network, you may order multiple SIP trunks. Infobip call routing allows you to define routes that consist of SIP trunks and phone number entries. You can have up to 10 entries in a route. Incoming calls to an Infobip DID can be forwarded to a designated route and thereby trigger a hunting sequence. When building your route in Infobip call routing, the last entry in your route can be a phone number. Upon loss of connectivity to your SIP trunks defined in that route, calls destined to the DID are automatically forwarded to the number you designate.There is no additional charge for using Infobip call routing, but regular per-usage rates apply for the traffic resulting from routing.For more information, see Call routing. |
Service address
Service address, also called Place of Primary Use (PPU), is the physical location where the SIP trunk service is primarily used or where the majority of the service is consumed. Specifically, it is the location of your SIP terminating equipment (SBC, PBX) connected to Infobip data centers. It is an important concept for regulatory and taxation purposes in the telecommunications industry, especially in countries such as the United States, for the following reasons:
- Taxation: telecommunications services in the United States are subject to various taxes and fees imposed at the federal, state, and local levels. The specific tax rates and regulatory requirements can vary based on the location where the service is being utilized. By specifying the service address or primary place of use, service providers can accurately determine the applicable taxes and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
- Regulatory Compliance: the telecommunications industry in the United States is regulated by various federal and state agencies. Compliance with these regulations is essential to ensure fair competition, consumer protection, and adherence to industry standards. The service address information helps service providers demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and jurisdictional boundaries.
- Jurisdictional Boundaries: telecom services can have jurisdictional implications, especially when crossing state or local boundaries. Determining the service address helps determine which regulatory requirements apply and ensures that services are appropriately governed and regulated based on the specific jurisdiction in which they are being provided.
For customers planning to consume SIP trunking services in the United States (PPU is in the United States and is independent of the Infobip data center to which you are connecting), it is mandatory to have a service address associated with your site trunk. For customers configuring SIP trunks outside of the United States with a PPU outside of the United States, associating a service address to a trunk is not mandatory but strongly recommended for documentation purposes.
Managing service addresses
You can manage service addresses using the Infobip web interface. Log in to your account and go to Channels and Numbers > Channels > Voice and WebRTC > SIP Trunking > Service Addresses.
Note the following:
- The same service address can be associated with multiple SIP trunks.
- A service address can not be deleted as long as it is associated with at least one SIP trunk.
- When a SIP trunk has been created, you may not change the associated service address.
The association of a service address to a SIP trunk is performed during the definition of the trunk.
Setting up a SIP trunk
SIP trunks can be created and managed using the Infobip web interface and API.
When you create a static trunk, your telephony system must expose public, fixed IP addresses. The following schema helps to clarify what is meant by source IPs and destination IPs.
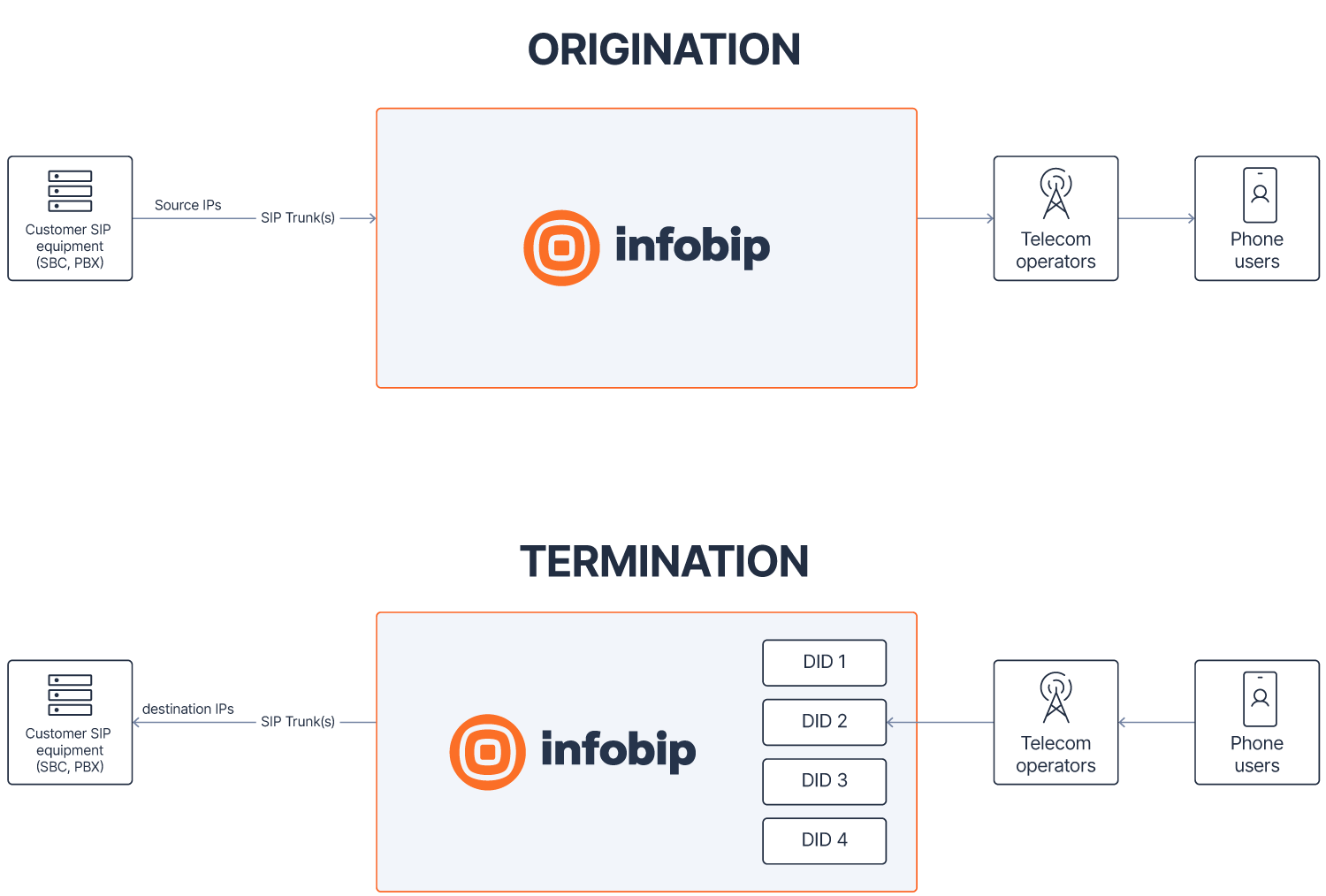
If a static SIP trunk definition does not include at least one source IP, then SIP traffic cannot be sent from your equipment to the Infobip infrastructure. Similarly, if a SIP trunk definition does not include at least one destination IP or FQDN, then incoming voice traffic to the Infobip platform can't be forwarded over your SIP trunk.
For registered SIP trunks, ensure that your Private Branch Exchange (PBX) is compatible with registered trunks.
Using the Infobip web interface
SIP trunks are managed from the Infobip web interface.
Go to Channels and Numbers > Channels > Voice and WebRTC > SIP Trunking.
If you intend to create a trunk in one of our USA data centers and/or have your Place of Primary Use (PPU) in the United States, ensure that you declared a service address first (see Service addresses).
Choose the SIP trunk provider
Click the CREATE SIP TRUNK button and select the type of trunk (trunk provider) you wish to provision. See Supported SIP trunk types and characteristics for more information.
For SIP trunks others than Infobip (that is, Freshworks, Genesys PureCloud, and so on), see Specific notes for provider trunks.
Choose plan and options
Choose between a Metered or Unlimited channel plan. For more information about these channel plans, see SIP trunk channels and related billing plans. Note that SIP trunk plans need to be activated on your account. If the plan selection is greyed out, contact your account manager or Support.
Select the number of required channels.
Main trunk settings
Follow the wizard to complete the SIP trunk details. Depending on the SIP trunk provider (INFOBIP, FRESHWORKS, and so on) and type (registered, static), the following fields may need to be completed:
| Parameter | Description | INFOBIP | FRESHWORKS |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIP trunk name | The name you wish to allocate to your new SIP trunk. This name is also used as a reference in your invoice. | X | X |
| SIP trunk type | Choose static or registered. See Supported SIP trunk types and characteristics to understand the differences between static and registered trunks. | X | |
| Datacenter location | Choose the Infobip data center in which the trunk should be provisioned. | X | X |
| Service address | The service address or Place of Primary Use (PPU) for your SIP equipment. | X | X |
| TLS encryption | Enables you to choose between UDP (TLS disabled) or TSL/SRTP (TLS enabled). | X | |
| Codec | Add all of the CODECs you want to use on this SIP trunk. If you add multiple CODECs, you can order them into your preferred priority. | X | |
| DTMF | Select how DTMF transcoding will be handled. | X | |
| Fax | Specify your preferred protocol for the transmission of fax calls. | X | |
| Number format | Choose the numbering format you want for this trunk:
| X | |
| International calls | Choose whether to block or allow calling to international numbers on this trunk. A call is considered to be international when A and B numbers are from different countries. | X | X |
| SIP Options | Request Infobip to send SIP Options to your SIP equipment. The sending interval is fixed to 60 seconds.Infobip always answers to SIP options that you send towards our infrastructure. The response sent back is always a 200 OK.For SIP OPTIONS, Infobip sends towards your infrastructure. If the SIP OPTIONS polling determines that your trunk is out of service, although that status is known to our infrastructure and taken into account for call routing, the OPTIONS status is not reflected on the Infobip web interface nor via the SIP trunk status API method. | X (static) | |
| Invite Challenge Authentication | When enabled, the platform performs an authentication challenge on each individual session. | X (registered) |
IP configuration
This configuration step appears only when configuring an INFOBIP static trunk.
Enter the list of source and destination IP addresses / FQDNs.
For destination IPs, if you do not have multiple redundant network elements, simply add your static IP, with the default SIP port of 5060. If you enter more than a single IP/FQDN, you may select the routing strategy to be applied:
- Failover: when sending calls to your SIP equipment, we will select destination IPs in the order they are configured. If the first IP is unavailable, we will select the next one, and so on.
- Round robin: when sending calls to your SIP equipment, we will select destination IPs in the order they are configured. Round robin is best used with symmetrical trunks (that is, trunks with the same capacity).
For source IPs, specify all the IP addresses from which you will source traffic to our network. These may be different from the destination IPs.
Review order
Review all settings, then go on with the confirmation of the trunk creation. You may navigate back to previous steps if you wish to change any value.
When you click Pay now, your creation request is submitted to our system and a dialog displays the IP addresses of our primary and backup SBCs (see SIP trunking redundancy). You should safelist the Infobip SBC IP addresses on your infrastructure to ensure the traffic can be processed on both sides. For registered trunks, this dialog also includes your username and password.
Make sure that you take note of your username and password and keep them in a safe place.
Once you acknowledge this dialog, you are brought back to your list of SIP trunks. Monitor the Admin and Action status. See Understanding SIP trunk status.
Retrieving your authentication (registered trunks)
For registered trunks, your username and password are given in the last final dialog when creating the trunk. If you have lost your credentials or fear these might have been compromised, you must request for new credentials. From your SIP trunk list, click on your registered trunk and click on the button to reset your password. A popup dialog will provide you both username and new password.
Using API
For more information about the API methods used for managing locations and SIP trunks, see Calls API platform (opens in a new tab).
Understanding SIP trunk status
| Status class | Status value | Description | Applies to |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administrative | ENABLED | The SIP trunk is enabled for use by the user. | Static & Registered trunks |
| Administrative | DISABLED | The SIP trunk is disabled for use by the user. Calls sent to this trunk will not be processed. For registered trunks, setting the administrative status to disabled will force the deregistration of any registered clients. | Static & Registered trunks |
| Administrative | SYSTEM_DISABLED | The SIP trunk has been disabled by the system and cannot be re-enabled by the user unless the root cause has been fixed. When the root cause is fixed, the trunk will be transitioned back to the disabled state. From that moment, the user can re-enable the trunk as required. | Static & Registered trunks |
| Registration | REGISTERED | At least one client is registered on the trunk. | Registered trunks |
| Registration | UNREGISTERED | No client is registered on the trunk. | Registered trunks |
| Action | PENDING | The submitted action (create, edit) has been submitted and its status is pending. No further action can be submitted until this action completes. | Static & Registered trunks |
| Action | SUCCESS | The submitted action (create, edit) has been successfully completed or applied. | Static & Registered trunks |
| Action | RESET | The submitted action (edit) could not be completed and the trunk has been restored to its pristine state. | Static & Registered trunks |
| Action | FAILED | The submitted action (edit) could not be completed and the outcome has turned the trunk into an unusable state. No traffic is allowed on this trunk and the only possible user action is to delete the trunk definition. | Static & Registered trunks |
Infobip SBC locations
When creating a SIP trunk the system will return the primary and secondary Infobip SBC IP addresses you should configure on your environment.
For documentation, here is the list our main SBC IP addresses by data center.
| Location name | Geography | Infobip static trunk SBC address | Infobip registered trunk SBC address |
|---|---|---|---|
| FRANKFURT | Frankfurt, Germany | 62.140.31.124 | 62.140.31.213 |
| BOGOTA | Colombia | 81.23.252.124 | 81.23.252.80 |
| NEW_YORK | New York, US | 185.255.9.23 | 185.255.9.216 |
| PORTLAND | Portland, US | 185.255.11.170 | 185.255.11.110 |
| SAO_POLO | Sao Paolo, Brazil | 81.23.253.104 | 81.23.253.60 |
| SINGAPORE | Singapore | 81.23.254.103 | 81.23.254.222 |
| JOHANNESBURG | Johannesburg, South Africa | 202.22.162.104 | 202.22.162.50 |
| MOSCOW | Moscow, Russia | 202.22.163.127 | 202.22.163.222 |
| ISTANBUL | Istanbul, Turkey | 202.22.169.124 | 202.22.169.222 |
| KUALA_LUMPUR | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia | 202.22.165.100 | 202.22.165.222 |
SIP trunk creation limitations
By default, a single Infobip account can have:
- Up to 10 trunks per account.
- Up to 10 trunks per Infobip data center.
- Up to 3 IP addresses per trunk for inbound traffic.
- Up to 3 IP addresses per trunk for outbound traffic.
- SIP trunks in up to 2 different Infobip data centers.
Setting up call routing
In this context, you rent one or several numbers from Infobip and would like calls received on these numbers to be forwarded to your telephony equipment over your newly created SIP trunk(s). Infobip call routing is the Infobip product with which you can implement such scenario.
Specific notes for provider trunks
The following information is relevant to the specific provider trunks only.
Freshworks trunks
Freshworks provider trunks allow you to use Freshworks services (call center Freshcaller (opens in a new tab)) while leveraging Infobip as the underlying voice connectivity provider for both inbound and outbound calls.
Freshcaller uses Twilio as its communication engine. To use Infobip for voice connectivity with Freshcaller, you must:
- Configure a Bring Your Own Carrier (BYOC) connection with Twilio
- Have a properly configured Freshworks account
Follow the official Freshworks documentation (opens in a new tab) for setup instructions.
To set up an Infobip provider trunk for Freshworks, you must provide these two specific parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Twilio Account SID | Your Twilio Account SID. |
| Destination Host | Your Twilio SIP domains (FQDN), as received from Freshworks. |
When defining multiple Freshworks trunks in the same Infobip data center, you should consider the following specific behaviors:
- Channels
- On inbound traffic (origination): The channel count defined per SIP trunk is applied as a channel upper limit on each individual trunk.
- On outbound traffic (termination): The total channel count for all defined Freshworks trunks is applied as an upper group limit across all Freshworks trunks.
- Reports and Logs
- On inbound traffic (origination): Reports and logs show the SIP trunk ID and SIP trunk name used for sending traffic to Freshworks.
- On outbound traffic (termination): Reports and logs show the ID and name of the oldest provisioned Freshworks trunk. This is because traffic from Freshworks does not include a trunk identifier.
Genesys PureCloud trunks
See the Genesys PureCloud Provider SIP Trunk Configuration Guide (opens in a new tab) to help you setup a Genesys PureCloud trunk and configure it in Genesys PureCloud.
You can determine the appropriate region where the SIP trunk needs to be created based on your Genesys PureCloud web interface login URL:
Cisco Webex trunks
See the Cisco Webex Provider SIP Trunk Configuration Guide (opens in a new tab) to help you setup a Cisco Webex trunk and perform the Cisco Webex BYOC Enterprise configuration.
OpenAI Realtime SIP trunks
Configuring a trunk to bring Infobip voice to OpenAI Realtime API over SIP only requires that you provide your OpenAI Project ID.
To connect Infobip voice to the OpenAI Realtime API over SIP, you only need to provide your OpenAI Project ID.
- Infobip OpenAI Realtime SIP trunks integrate directly with OpenAI. These trunks do not support OpenAI Realtime deployments on Azure.
- You can create OpenAI SIP trunks in any listed Infobip data center. Infobip does not control which OpenAI data center or region will be triggered.
Connect inbound caller to your AI agent
Use Infobip Call Routing to connect inbound callers to your OpenAI Realtime project.
To set this up, follow these steps:
- Create a new route in Call Routing and set your OpenAI trunk as the destination.
- Configure the route based on how users will call your agent:
- PHONE: Ensure you have at least one Infobip DID. For detailed steps, see Call Routing documentation.
- WHATSAPP: Make sure you have at least one WhatsApp sender enabled for WhatsApp Voice. The setup is similar to phone, but inbound configuration is done from the WhatsApp Voice tab of your sender in the Numbers application on the web interface.
- WEBRTC: Refer to the filter-based route execution documentation. In summary:
- Your WebRTC client (using Infobip's WebRTC JS or mobile SDK) must place an applicationCall to
CALL_ROUTING. - Your route in Call Routing must have a filter criteria defined of type
WEBRTC.
- Your WebRTC client (using Infobip's WebRTC JS or mobile SDK) must place an applicationCall to
Enable your AI agent to call recipients
Outbound calls from OpenAI to Infobip over the SIP trunk are not supported directly. To enable your AI agent to call recipients, build a voice application using the Calls API platform.
This application:
- Creates the outbound call to the recipient(s), either as an individual call (opens in a new tab) or bulk calls (opens in a new tab).
- When the call is answered, connect it to an outbound SIP call to your AI agent by:
- Using the create Dialog (opens in a new tab) method.
- Setting the
childCallRequestto use theSIPendpoint type and referencing your OpenAI trunk'ssipTrunkId.