Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a part of artificial intelligence (AI). NLP interprets human language and converts unstructured end user messages into a structured format that the chatbot understands. NLP uses techniques such as tokenization to do this.
NLP is available only for the User Response element in AI chatbots.
Tokenization
Tokenization is an NLP feature. Tokenization breaks the user input into discrete pieces of information. Tokenization includes the following:
- Autocorrection of words
- Autocompletion of words
- Removal of stop words
- Matching of synonyms
Autocorrection
If an end user's message contains spelling errors, Answers corrects these errors.
Example: The end user's message contains the incorrect spelling 'emali'. Answers auto corrects the input to 'email'.
If a word is autocorrected incorrectly, Answers can identify the wrong intent. If you find that Answers has autocorrected a word that does not need autocorrection, add a training phrase that contains the original word (before autocorrection) to the correct intent. So, Answers will not autocorrect this word again.
Autocompletion
If an end user's message contains incomplete words, Answers completes these words.
Example: The end user's message contains the incomplete word 'emai'. Answers auto completes the input to 'email'.
Removal of stop words
When the chatbot processes the end user's message, it filters out (stops) certain words that are insignificant. This filtering increases the accuracy of the chatbot to identify the correct intent.
The inbuilt stop list in Answers contains stop words for the following languages. For other languages that Answers supports, there are no stop words.
Language | Stop words |
|---|---|
| English | a, an, and, are, be, do, have, i, in, is, me, of, that, the, to, you |
| Spanish | a, al, como, con, de, del, el, en, es, eso, ha, la, las, le, lo, los, mas, me, mi, nos, o, para, pero, por, que, se, si, son, su, sus, un, una, y, yo |
| Croatian | a, ali, cu, da, do, i, ili, iz, je, k, ka, kako, li, me, mi, mogu, na, nego, ni, niti, no, o, od, pa, po, s, sa, sam, se, su, te, to, u, uz, vec, za |
| Arabic | أن, عن, كيفية, يوجد, اود, إلى, في, أنت, هو, مع, هي, شو, هم, على, كيف, ما, أنا, هذا, هل, أو, لو, أستطيع, سمحت, التي, بدي, إذا, و, ذلك, أعلم, فقط, به, بها, بهذا, عليها, عليه, بعض, اريد, لكن, هنا |
| Portuguese | The chatbot removes accent marks when identifying stop words in the end user's message.a, ante, aos, apos, as, ate, com, contra, da, das, de, desde, do, dos, e, ela, elas, ele, eles, em, entre, essa, essas, esse, esses, esta, estas, este, estes, eu, isso, isto, lhe, lhes, lo, me, na, nas, no, nos, nossa, nossas, nosso, nossos, num, numa, numas, nuns, o, os, para, perante, por, que, sao, se, sem, seu, seus, sob, sobre, sua, suas, te, teu, teus, tras, tu, tua, tuas, um, uma, umas, uns, voce, voces, vos |
Synonym matching
End user messages may not necessarily contain the words that are in the training dataset of intents. Instead, the messages may contain a synonym of a word in the training dataset. Answers uses the inbuilt set of synonyms to match the end user's message with the correct intent.
Synonym matching is applicable only for English.
Example: The training dataset of the Baggage intent has the word 'baggage' but not the word 'luggage'.
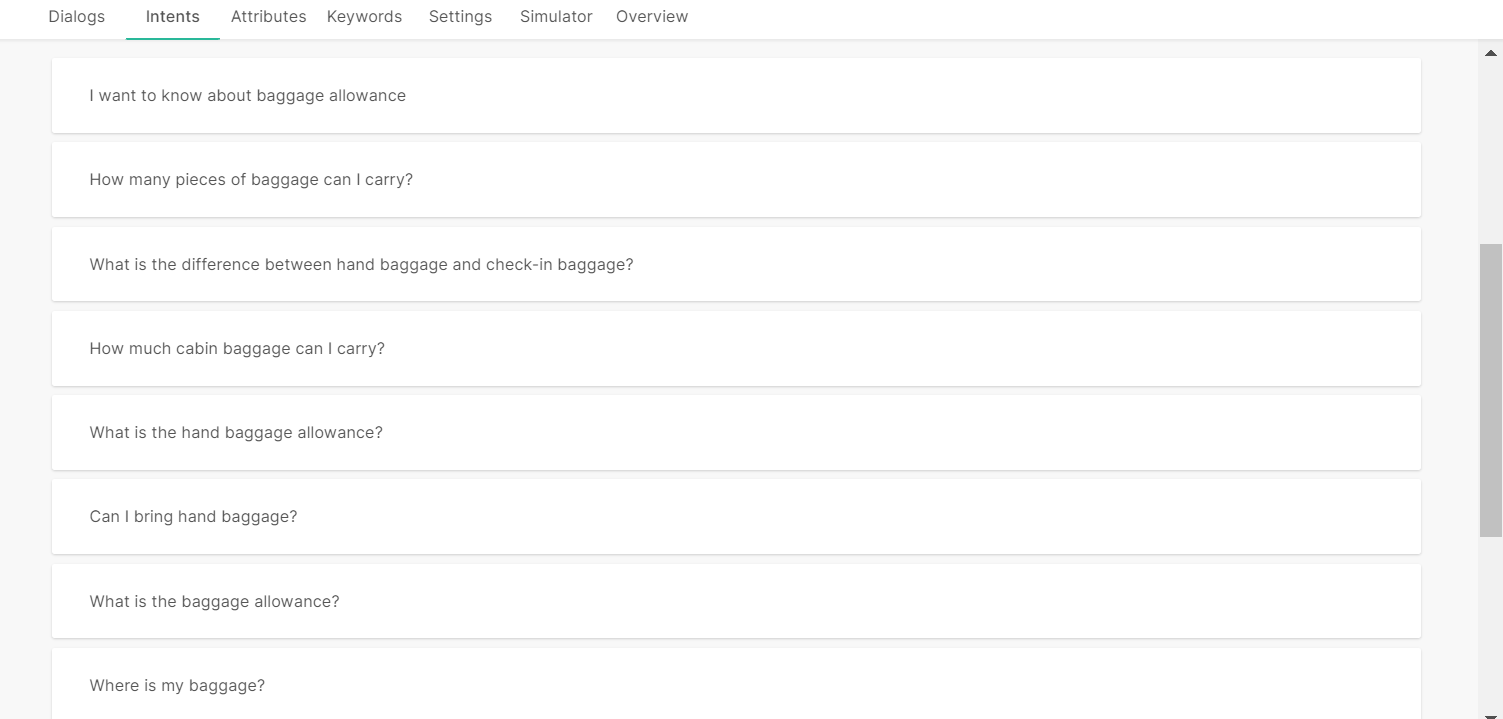
If the end user sends the message 'I want to know about luggage allowance', the chatbot uses the inbuilt synonym list and identifies that 'luggage' is a synonym of 'baggage'. The chatbot matches the end user's message with the training phrase 'I want to know about baggage allowance', and matches the message with the Baggage intent.
Example of tokenization
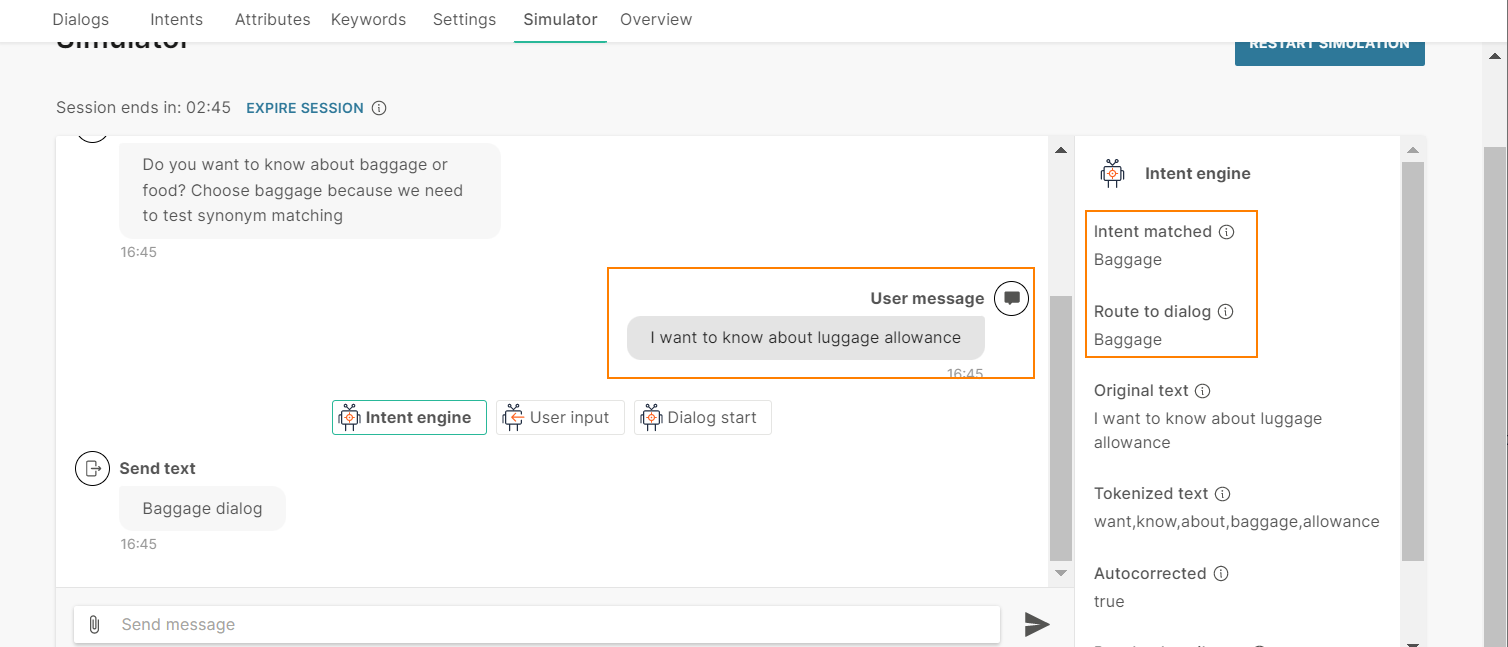
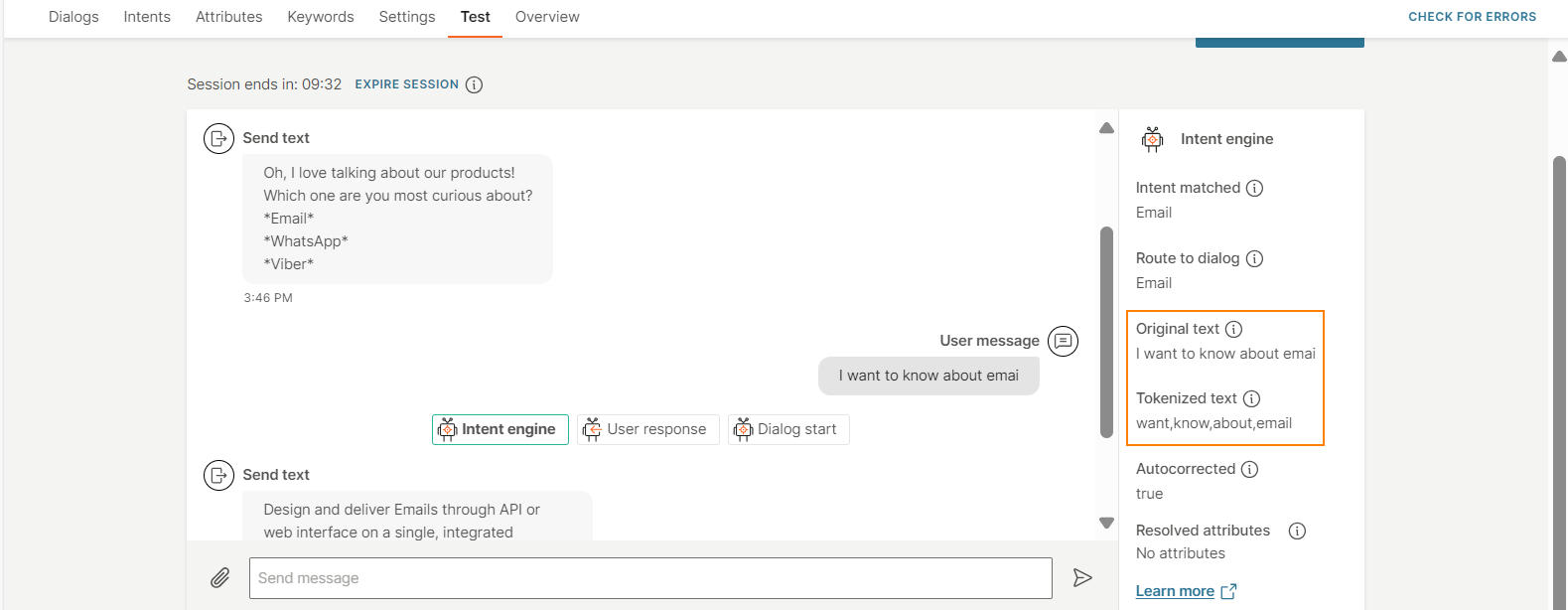
The end user sends the message 'I want to know about emali'.
The chatbot tokenizes the text as follows:
- It breaks the end user's message into separate words.
- It removes the stop word 'I'.
- It autocorrects the word 'emali' to 'email'.
So, the tokenized text is 'want', 'know', 'about', 'email'.
How Natural Language Processing Works
NLP is available only for the User Response element in AI chatbots.
When an end user sends a message, the chatbot first processes the keywords in the User Response element. If there is a match between the end user's message and a keyword, the chatbot takes the relevant action. If there is no match, the chatbot uses NLP.
- The chatbot tokenizes the text.
- The chatbot compares the tokenized text with the intents.
- When there is a match with an intent, the chatbot directs the flow to the dialog that is associated with that intent.
Example: Consider a chatbot that provides information about Infobip products.
For each product, there is a dialog. Each dialog has an associated intent. Example: For the Email product, there is an Email dialog, which has an Email intent.
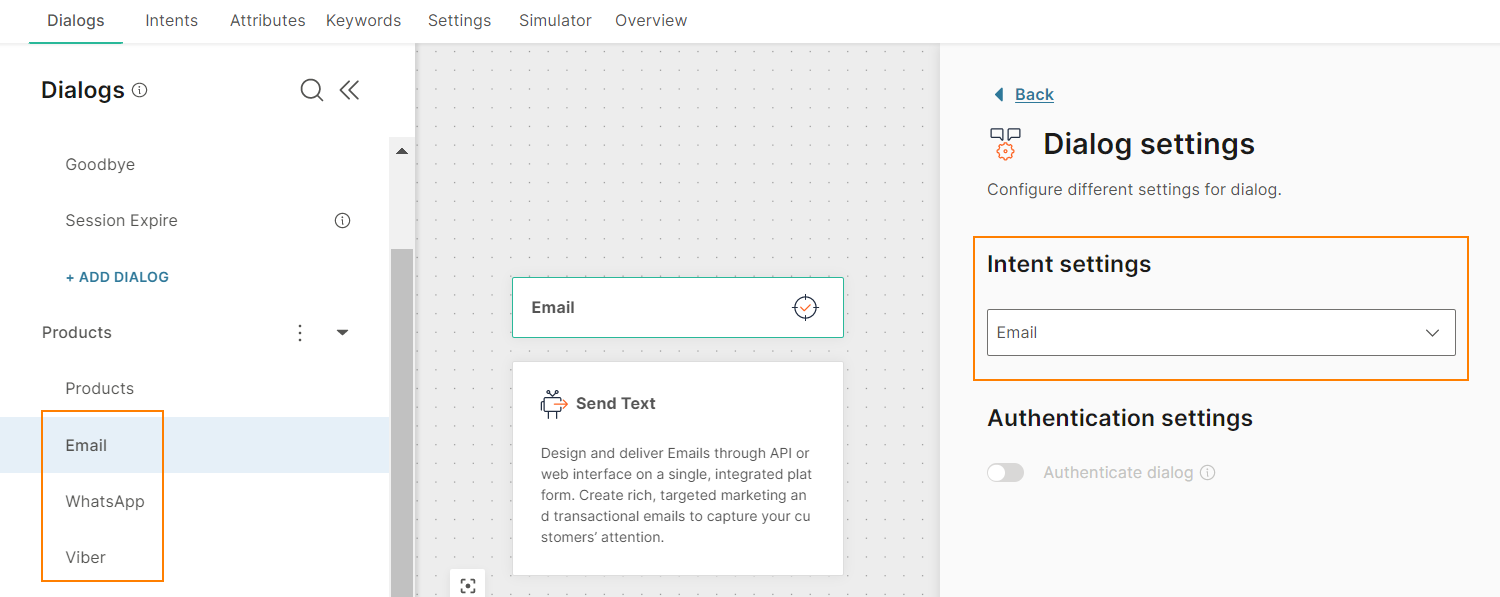
In the Products dialog, the User Response element uses keywords to branch the flow to the relevant dialog.
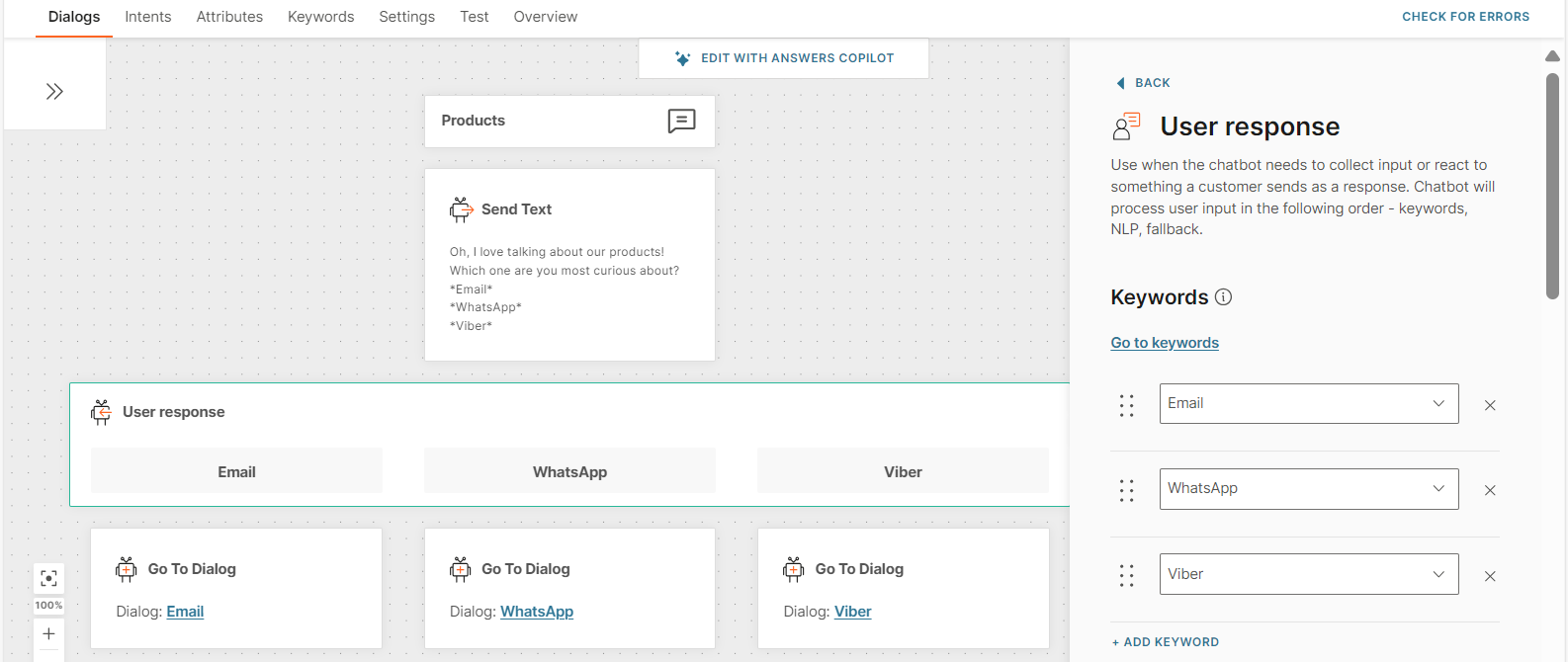
Without NLP enabled
The end user sends the message 'emali'. Because the message contains a spelling error, the chatbot is unable to match the user input to the keyword 'email'. So, the chatbot does not route the flow to the Email dialog.
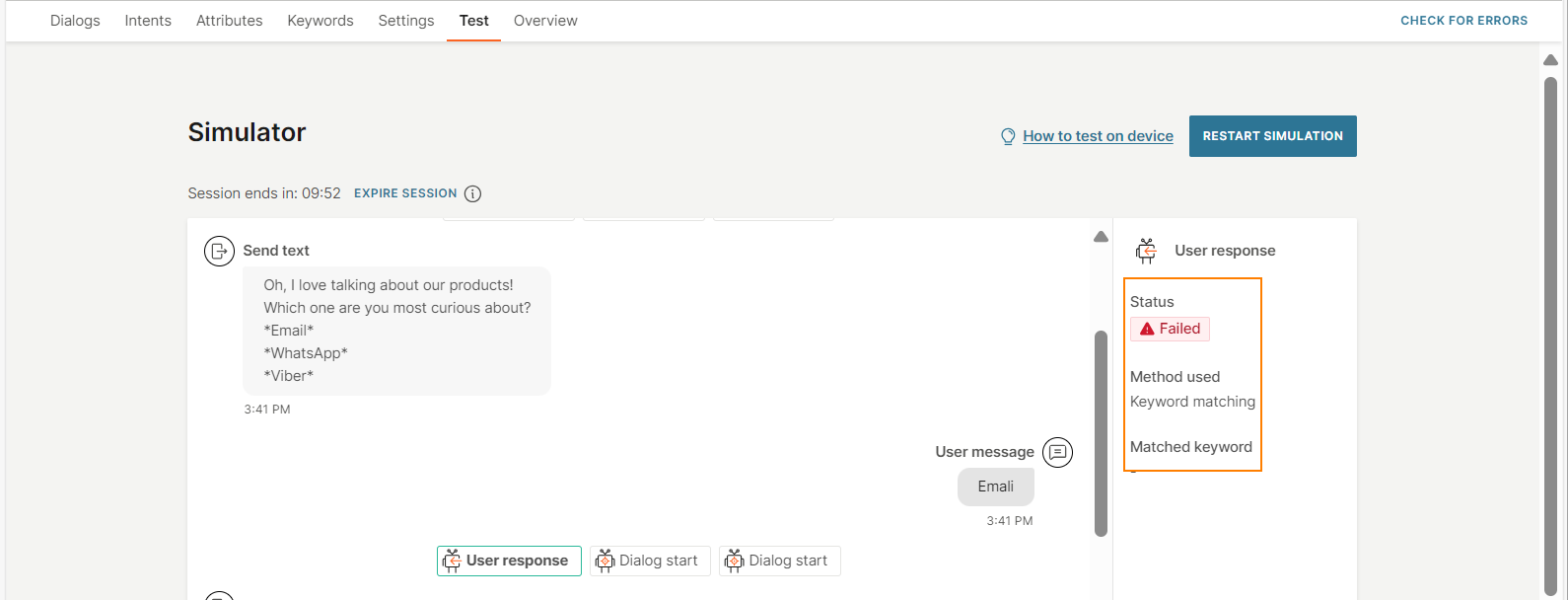
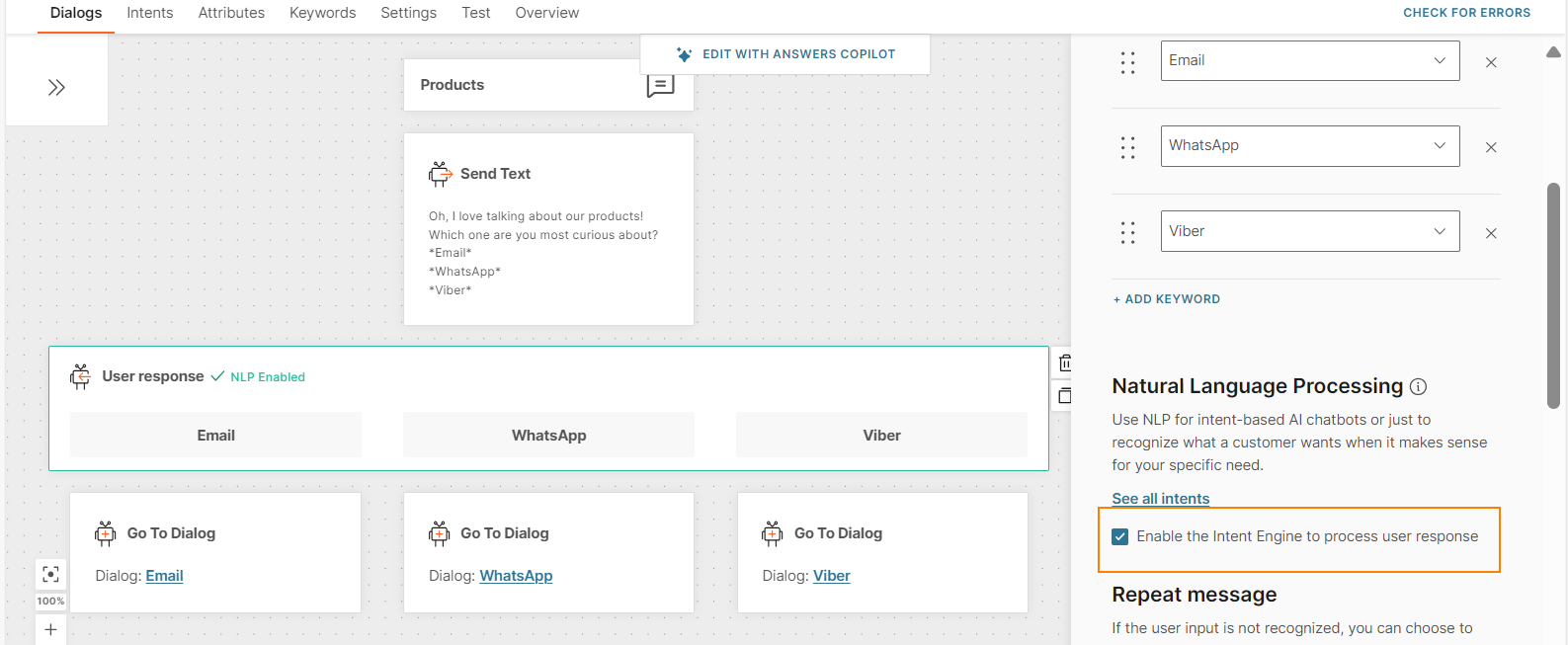
With NLP enabled
The User response element in the Products dialog has NLP enabled.
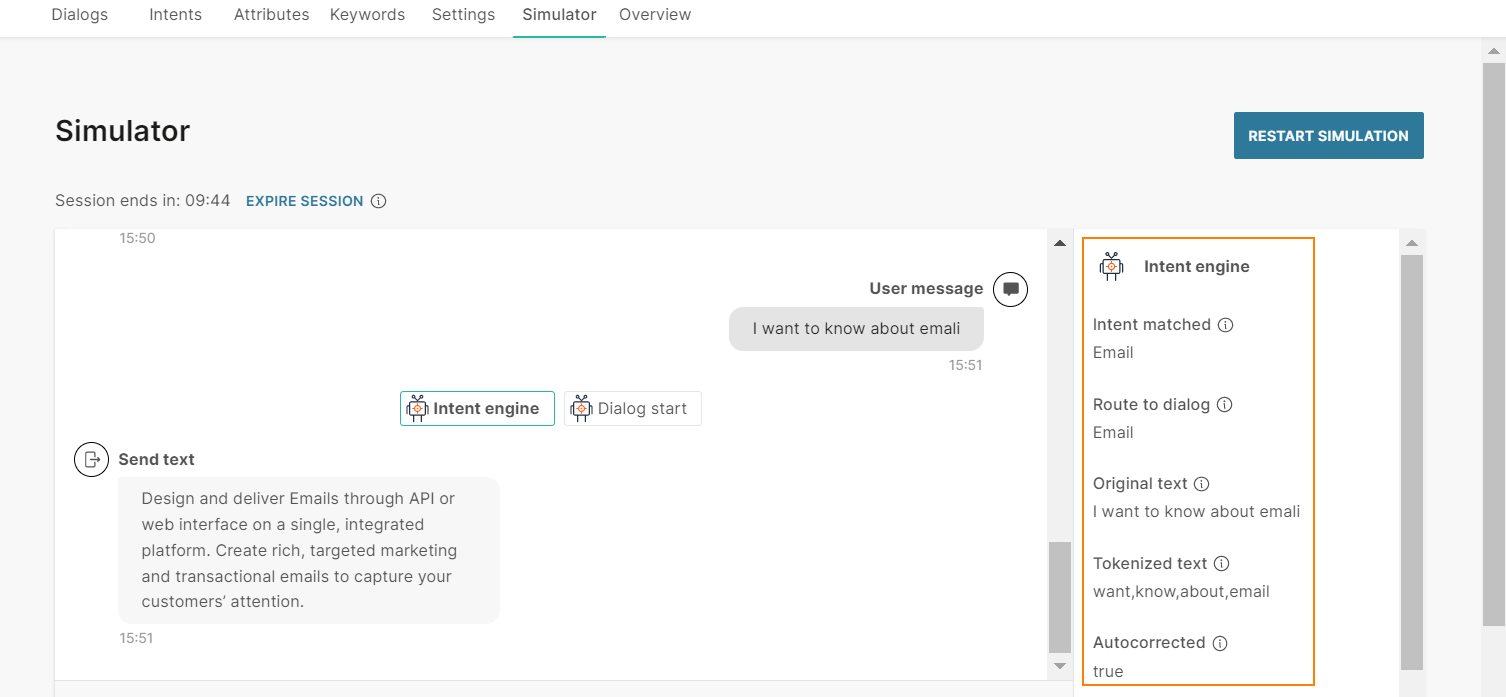
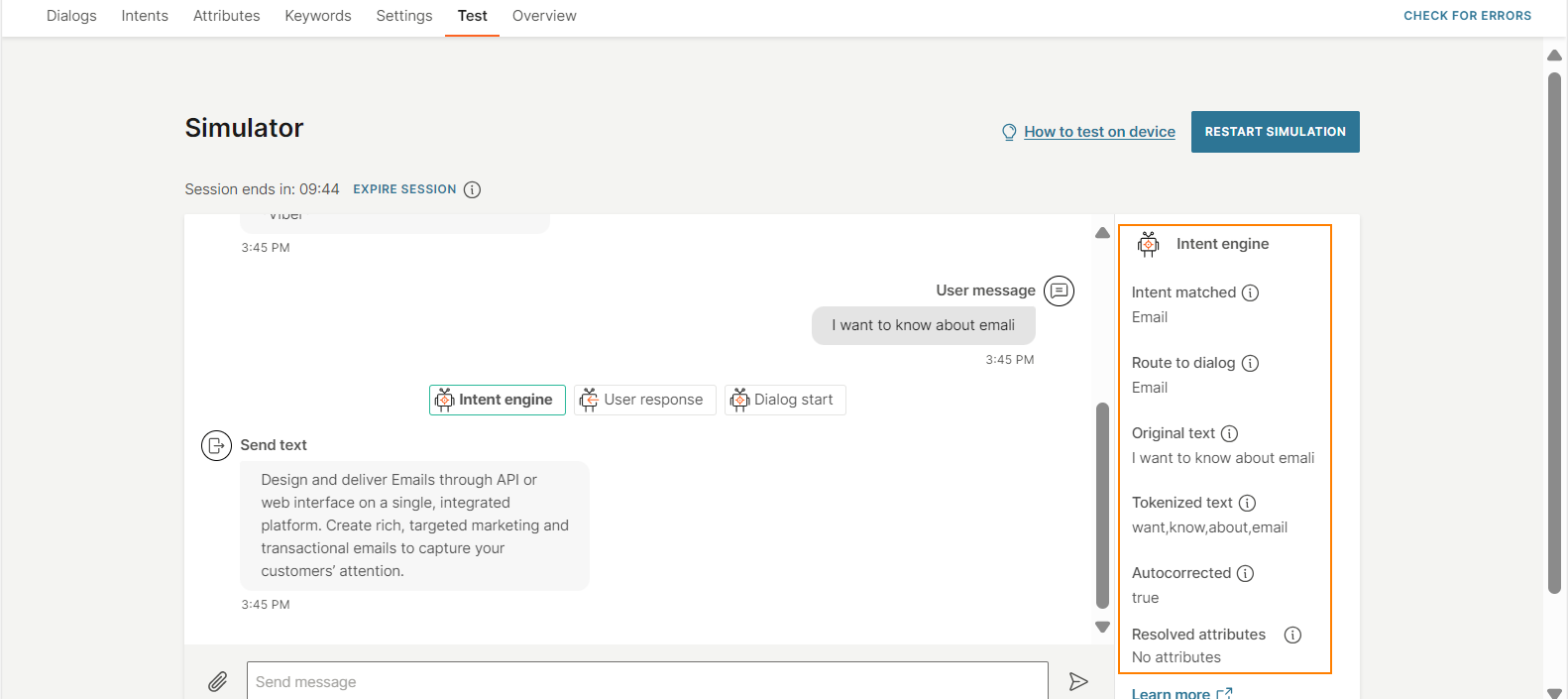
The end user sends the message 'I want to know about emali'.
The chatbot first processes the keywords in the User response element. The chatbot is unable to match the end user's message with any of the keywords. So, the chatbot uses NLP. The chatbot does the following:
- As part of tokenization, the chatbot autocorrects the word 'emali' to 'email'.
- The chatbot matches the tokenized text with the Email intent.
- It routes the flow to the Email dialog.
Similarly, if the end user sends the message 'I want to know about emai', Answers autocompletes the word 'emai' to 'email' and matches the tokenized text with the training dataset for the Email intent.
Enable natural language processing
You can enable NLP only for the User response element. Select Enable the Intent Engine to process user response.

The User response element indicates that NLP is enabled.
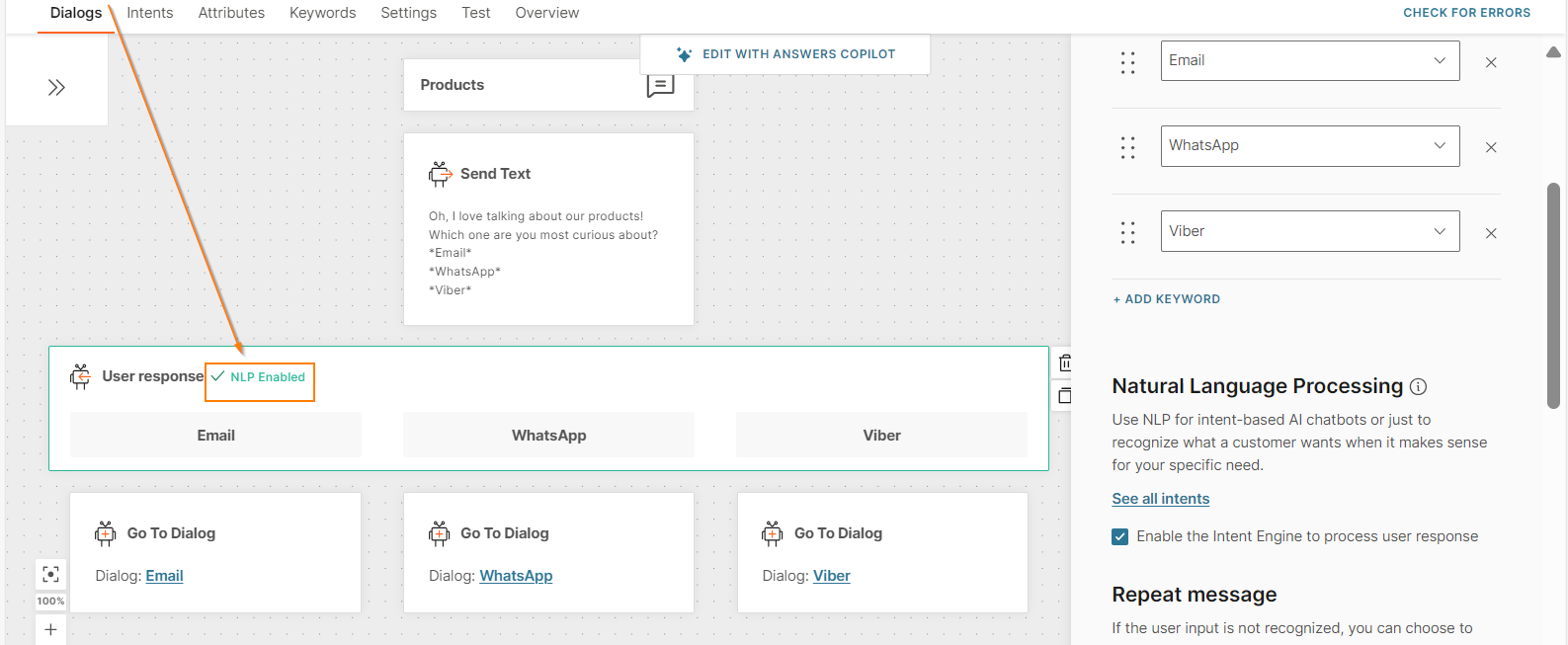
Do not enable NLP if you want the end user to select only from the options that you provide.
Test natural language processing
Use the simulator to test how well NLP works in an AI chatbot.
- Use synonyms of the words that you used to train the chatbot, and see how well the chatbot recognizes the intent. Example: If you train the chatbot with the word 'baggage', use the word 'luggage' in the simulator. Refer to the example shown in the Synonym matching section.
- Enter incomplete words or incorrect spelling of words that in training phrases to see how the chatbot corrects these errors. Refer to the How NLP works section.