Concepts
Templating Language
In order to facilitate the extraction of values and dynamic generation of content, we introduced a templating language – Liquid (opens in a new tab) - to the Answers platform.
Liquid is a templating language with simple markup, made so that users can edit it.
Use templating language in all fields in which you can enter text and variables, in Answers elements. Example: Text fields in Text element and List element.
Liquid code uses objects, tags, and filters in a template which is then rendered and the content is dynamically shown. Template is any message you create that contains templating language elements.
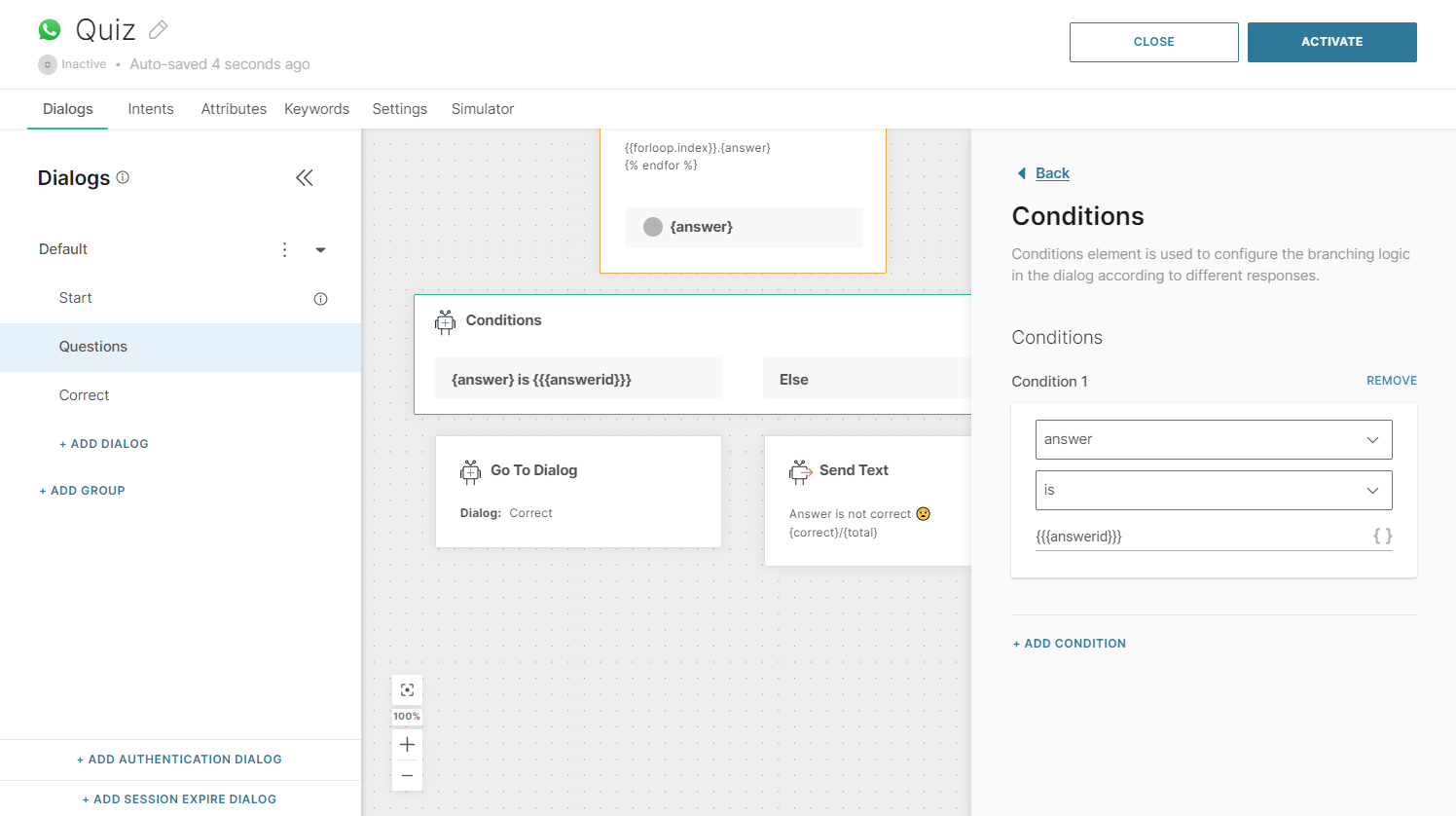
Objects
Objects are used to show content on a page. Objects and variable names are denoted by double curly braces: {{ and }}.
Types of objects: String, Number, Boolean, Nil, and Array.
More about Liquid objects (opens in a new tab).
Tags
Tags create the logic and control flow for templates. They are denoted by curly braces and percent signs: {% tag %}. Tags do not render into any visible text; you use them to assign variables and create conditions and loops in the background.
There are five different types of tags:
• Comment tags– use {% comment %} and {% endcomment %} tags to turn anything between them into a comment.
• Control flow tags– change the displayed information using programming logic: if, unless, elseif/else, case/when.
• Iteration tags – for, else, break, continue, plus additional tags for parameters (limit, offset, range, reversed), cycle, and tablerows (cols, limit, offset, range) to repeatedly run blocks of code.
• Raw tags – used to temporarily disable tag processing, {% raw %} and {% endraw %}.
• Variable tags – assign, capture, increment and decrement are used to create new variables in the templating language.
| == | equals |
| != | does not equal |
| > | greater than |
| < | less than |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| or | logical or |
| and | logical and |
Learn more about Liquid tags (opens in a new tab).
Filters
Filters change the output of the template language object. They are used within the object and are separated by a | (pipe) character. You can use multiple filters for one output applying them from left to right (each separated by the | character). Check the list of all available filters (opens in a new tab).
If you want to dive deeper into examples how to use templating language in Answers, check the How to section.
Regular Expressions
Regex (opens in a new tab) (regular expression) is useful in situations where you want to check, match, or validate different inputs, like check if a string contains numbers, or validate if the input is a phone number.
Use regular expressions in the Save user response and Code elements.
Here is a list of the most commonly used operations in Regex:
Character classes
. any character except newline
\w \d \s word, digit, whitespace
\W \D \S not word, digit, whitespace
[abc] any of a, b, or c
[^abc] not a, b, or c
[a-g] character between a & g
Anchors
^abc$ start / end of the string
\b word boundary
Escaped characters
. \* \ escaped special characters
Groups & Lookaround
(abc) capture group
\1 backreference to group #1
(?:abc) non-capturing group
(?=abc) positive lookahead
(?!abc) negative lookahead
Quantifiers & Alternation
a* a+ a? 0 or more, 1 or more, 0 or 1
a{5} a{2,} exactly five, two or more
a{1,3} between one & three
a+? a{2,}? match as few as possible
ab|cd match ab or cd
For information about how to use regular expression in your chatbot, refer to the How to section.